Post 2: Terra Cotta Facades
This is the second in a series of blog posts on historic and antiquated structural and façade systems. As discussed in Part 1 of this series on Historical Building Systems’ Series: Iron and Riveted Steel, inspection of these historic systems requires specialized knowledge from experienced forensic experts who can assist with the assessment, repair and retrofit of these systems.
This post focuses on terra cotta masonry as an example of such an historical system.
Terra Cotta Fundamentals
Terra cotta (which is sometimes written as a single word: terracotta) is a form of fired clay. It differs from brick and tile in that its raw material is finely milled clay from which most impurities have been removed. The resulting fine-grained texture allows for more refined and intricate details and sharper finishing. Terra cotta often has an outer surface, known as the fireskin, which is denser than the underbody. Terra cotta typically comes in various shades of buff, brown or red. It is commonly, but not always, glazed. The earliest forms of terra cotta date back to 10,000 BCE when terra cotta was utilized for Chinese pottery and has been utilized architecturally since ancient times in cultures around the globe.
Understanding Modern Terra Cotta
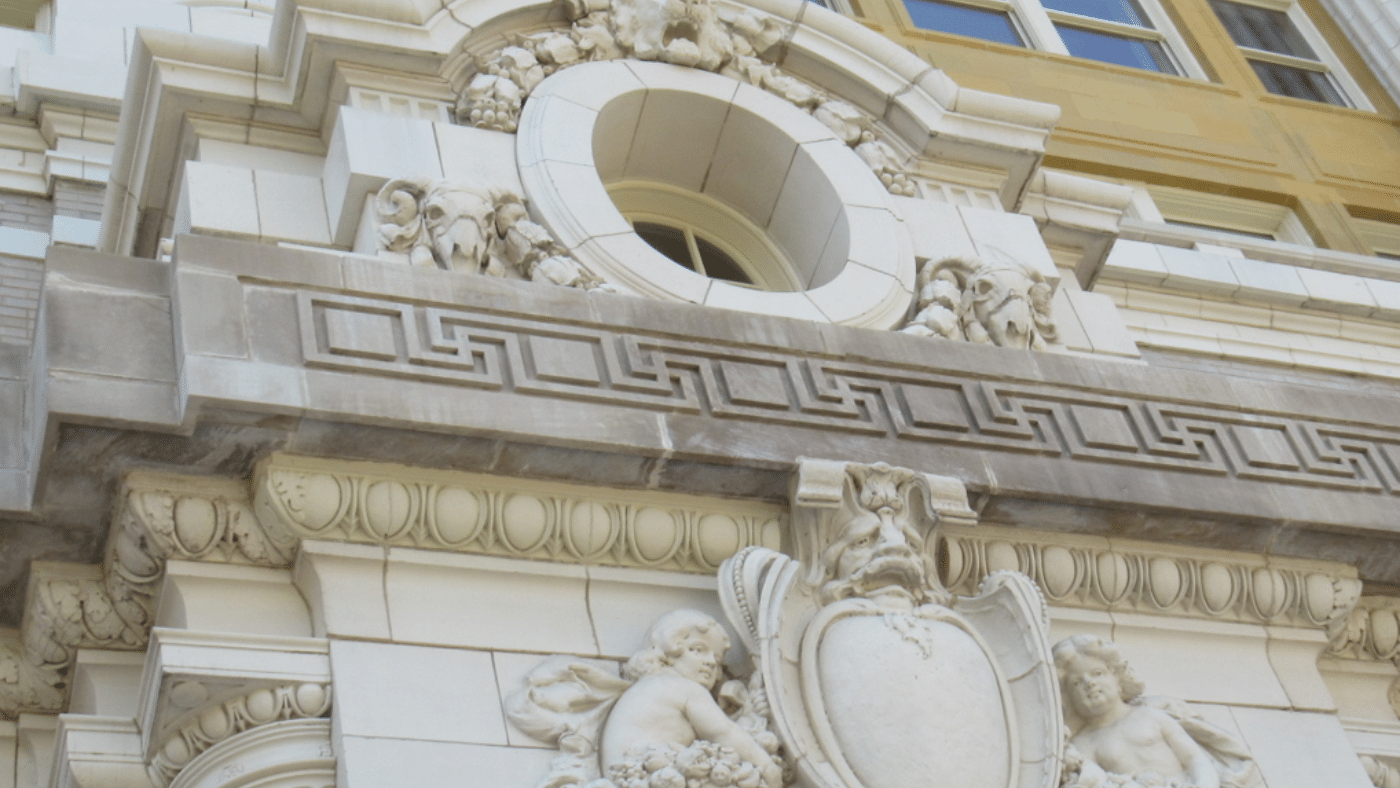
Terra cotta saw a resurgence of use in the 1700s in England and the 1800s in the United State of America. The material was utilized for its inherent fire resistance — a quality much sought after following the great Chicago fire of 1871 (Fig. 1 below). In addition, terra cotta components are moisture resistant, lightweight, moldable and reproducible.
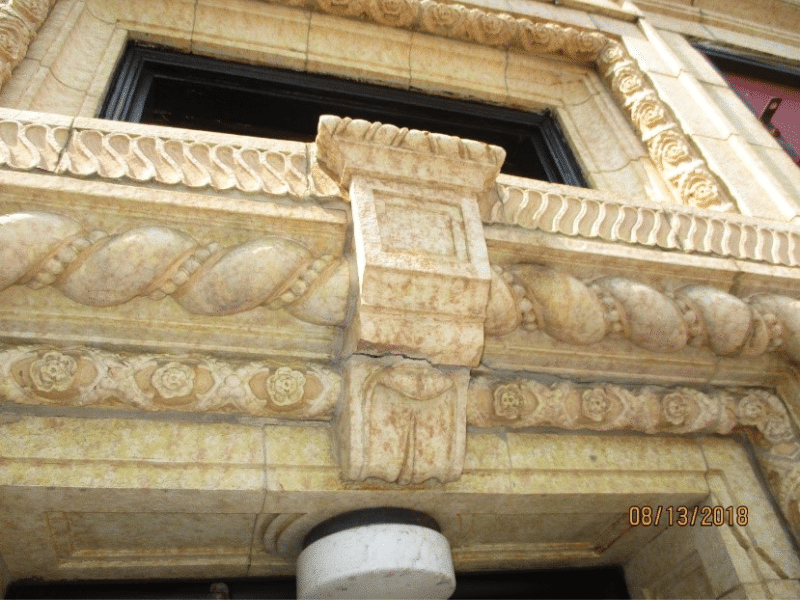

Figure 1: Intricate terra cotta detailing in Chicago, Illinois
Making Terra Cotta Components
Terra cotta can be formed in several ways. Terra cotta components are generally hand cast in individual molds, while more linear components, such as windowsills, ledges and crown moldings are formed in continuous slip castings using an extrusion process (Fig. 2 below). Terra cotta figureheads or similar features can also be hand crafted by individual artisans.
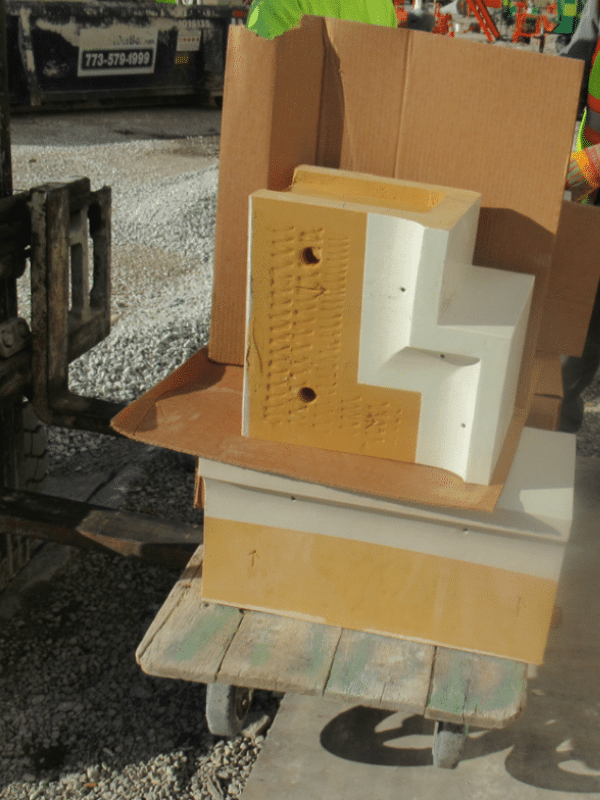

Figure 2: A newly cast terra cotta building cornice, ready for installation
In addition to façade components, terra cotta is commonly used for chimney liners and parapet wall capstones. As a fired clay product with few impurities, the material possesses a high resistance to heat, making it an ideal choice for exposure to the fire and smoke of a chimney.
Supporting Terra Cotta Components
Underlying structural steel frames and outriggers commonly support terra cotta building façade components. These structural steel components provide the tensile strength necessary to allow the terra cotta to elegantly cantilever outward. In turn, the fire resistance of the terra cotta protects the underlying structural steel. The resulting structure is relatively lightweight when compared to historic, all-masonry systems (Figs. 3 and 4).
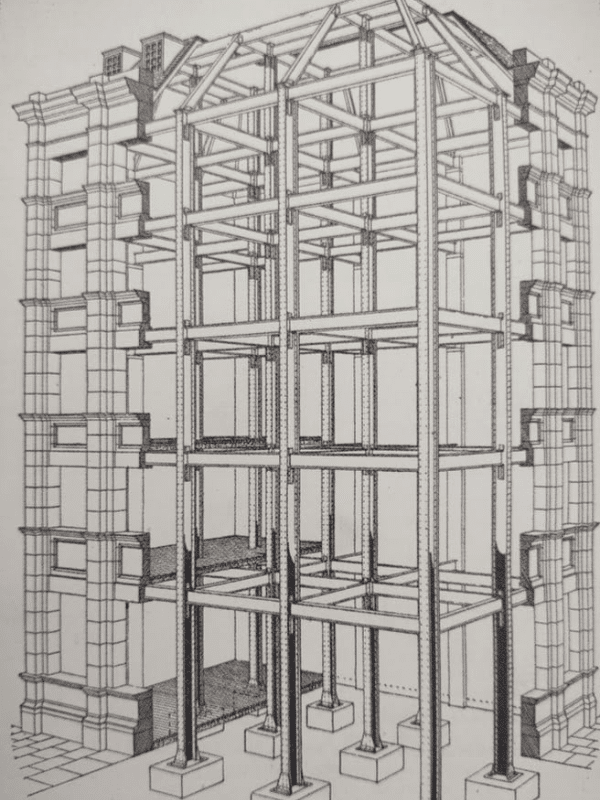
Figure 3: Steel frame visible behind a terra cotta façade, From Rivington’s Notes on Building Construction (1915)
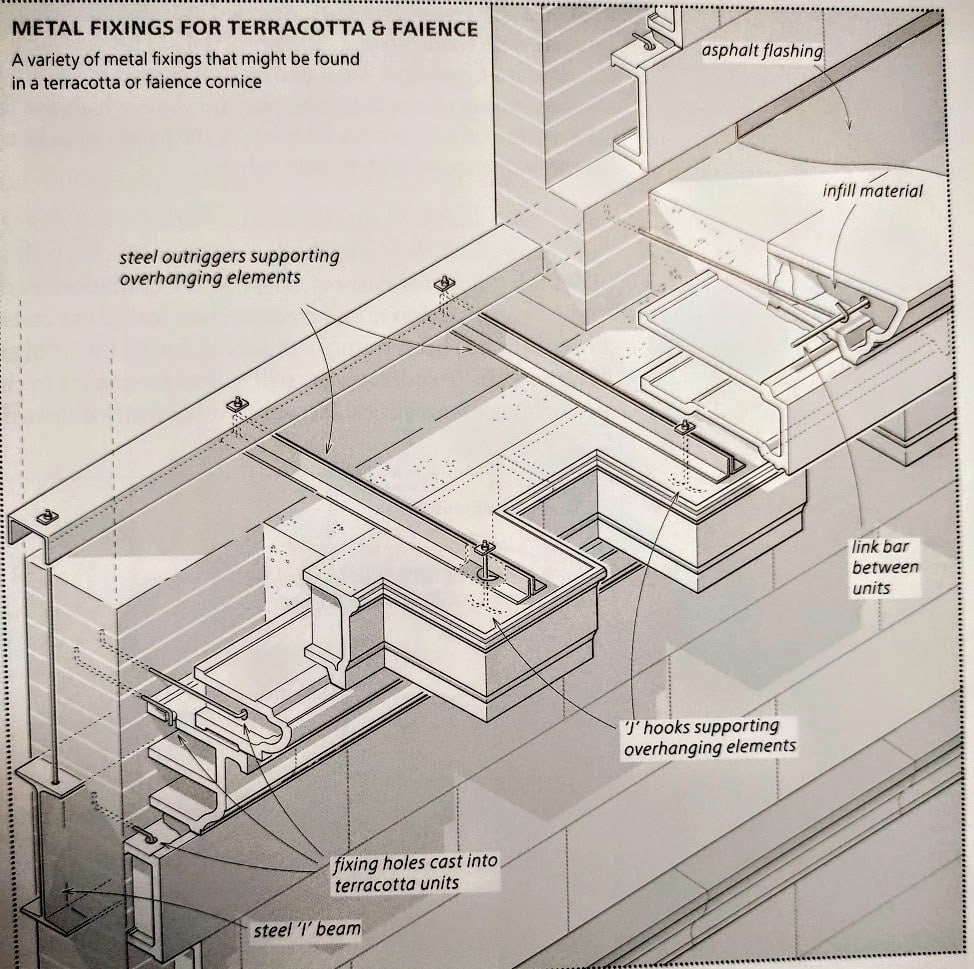
Figure 4: Terra cotta steel support framing, from Historic England Practical Building Conservation (2015)
Forensic Issues in Terra Cotta Structures
Terra cotta structures are susceptible to damage and staining from environmental factors such as long-term water intrusion and chemical exposure. Water intrusion can cause freeze-thaw damage, in which the expansive forces of frozen water causes cracks and spalling of the terra cotta. In addition, water intrusion can cause corrosion of underlying metal support components, another source of expansive stresses in the terra cotta. The material can also be damaged mechanically from impacts (Fig. 5 below), hail or from building movement, such as settlement. Once damaged, terra cotta requires skilled workers (Fig. 6 below) and cannot generally be repaired adequately by amateur or handy-man type workers. For this reason, the cost of repairs to an historic terra cotta structure may be greater than anticipated, based solely on the extent of observed damage.
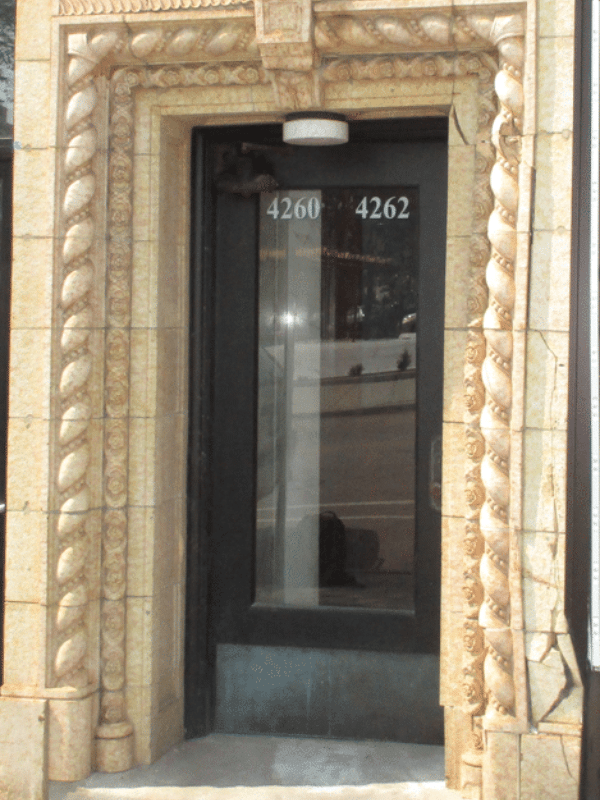

Figure 5: Damage to terra cotta entryway caused by vehicle impact.
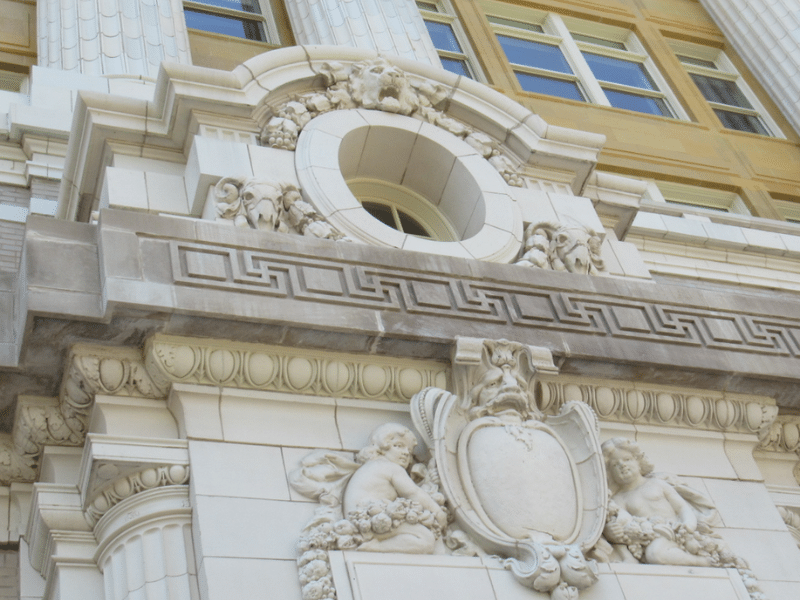

Figure 6: Terra cotta façade of the recently restored historic Cook County Hospital in Chicago, Illinois
How VERTEX Can Help
VERTEX has forensic experts as well as cost estimating professionals skilled in evaluating the unique characteristics of terra cotta structures and other historic elements. For more information on how to maintain, repair and restore them, contact Isaac Gaetz or submit an inquiry on our contact form.
In Part 3 of this series, we will discuss historic wooden trusses.




