What is Radon?
Radon is a naturally occurring, colorless, odorless, and tasteless radioactive gas that is produced from the natural breakdown of uranium in soil. Radon moves up through the rocks, soil, and groundwater into the atmosphere and emits alpha particles as it continues to naturally decay. Alpha particles are positively charged and made up of two protons and two neutrons from the atom’s nucleus and when inhaled may cause damage to living tissue. When examining properties for radon, the age and type of residential or commercial property don’t matter because radon is naturally occurring in the environment. Common routes of radon into your residential or commercial space are:
- Spaces between the basement walls and the lab of the structure
- Cracks in the foundation or walls
- Openings around sump pumps and drains
- Construction joints and plumbing penetrations
- Crawl spaces
- Well water with high radon concentrations
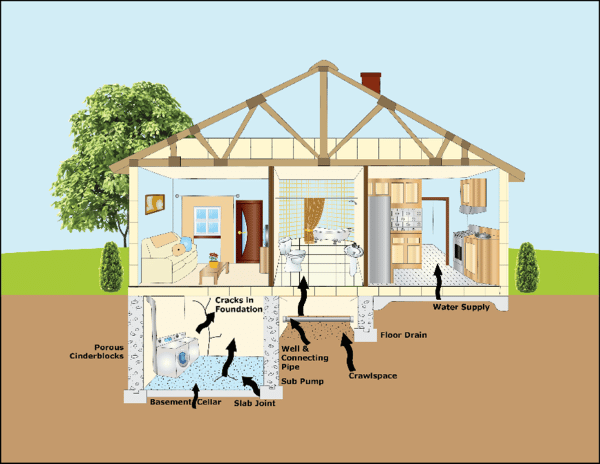
Figure 1: Radon routes of entry into a residential dwelling (Source: USEPA)
Health Effects of Radon
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer behind only cigarette smoking. The primary route of exposure to radon is through inhalation where radioactive particles can become trapped in the lungs. Chances of developing cancer as a result of exposure to radon are dependent on whether the individual is a smoker, the amount of radon that is present in the location, and whether there are other substances that contribute to indoor particulates, such as wood or coal burning. Currently, the majority of Colorado is listed as zone 1 on the Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) Map of Radon Zones which indicates that the probable indoor radon average is >4 picocuries per liter (pCi/L). However, the Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment (CDPHE) has listed the entire state (every county) as being in radon zone 1 where again, the probable indoor radon average is >4 pCi/L. A pCi is a unit of measurement for radioactive decay for radon and is one-trillionth of a curie. For size reference, see the chart below created by the Washington State Department of Health using a dollar analogy.
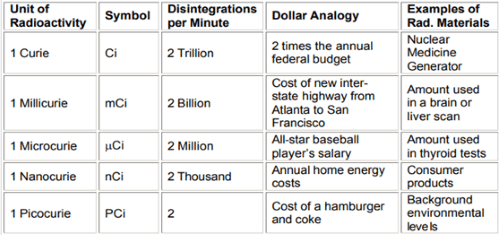
Figure 2: Table describing the size of a picocurie (Source: Washington State Department of Health)
EPA Radon Action Levels
EPA action level is 4 pCi/L for indoor radon, so it is recommended that residential and commercial spaces below the 3rd floor be tested every 2 years (EPA, 2016). EPA’s Map of Radon Zones is a good tool to reference when determining what zone a state falls in. The red shading represents zone one which indicates that those regions have the highest protentional for radon exposure and the average indoor radon levels may be greater than 4 pCi/L. The orange shading represents zone two which indicates that those regions have moderate potential for radon exposure and the average indoor radon levels may be between 2 and 4 pCi/L. Lastly, the yellow shading represents zone three which indicates that those regions have low potential and the average indoor radon levels may be less than 2 pCi/L. Be advised that local jurisdictions, like state health departments, for example, may have their own radon zone designations which might supersede EPA’s radon zone designation, as was previously demonstrated with the state of Colorado and CDPHE’s more stringent radon zone map for Colorado.
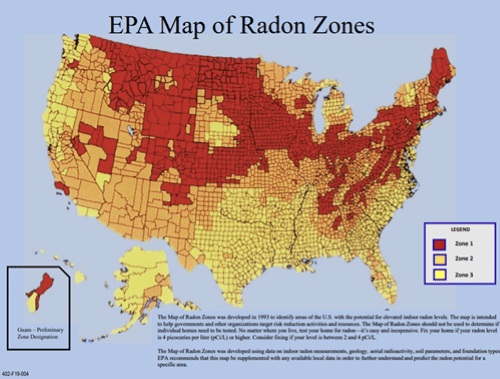
Figure 3: Map of Radon Zones (Source: USEPA)
Radon Inspections & Monitoring
The inspection process for determining how much radon is present can be done by conducting a short-term or long-term assessment. A short-term assessment is ideal for real estate transactions and can typically be done by either using a real-time Air Quality Monitor or a passive radon canister or badge and placing it in the lowest level of the property such as a basement or the first floor. It is recommended that the monitor/device be placed in an area that is occupied frequently such as a living room or a bedroom and ensure that all windows are closed. Long-term monitoring is ideal for understanding how radon gas levels fluctuate over time and in different seasons and which areas of the property are being affected the most.
How Can VERTEX Help?
VERTEX has experienced Industrial Hygienists and Environmental Consultants who can conduct Indoor Air Quality Assessments, including radon inspections, and work closely with accredited analytical laboratories to determine the amount of Radon present and provide professional guidance to ensure that commercial spaces are below the recommended levels of exposure.
To learn more about VERTEX’s Industrial Hygiene & Building Sciences services or to speak with an Environmental Expert, call 888.298.5162 or submit an inquiry.
Article Author: Monica Ortiz



