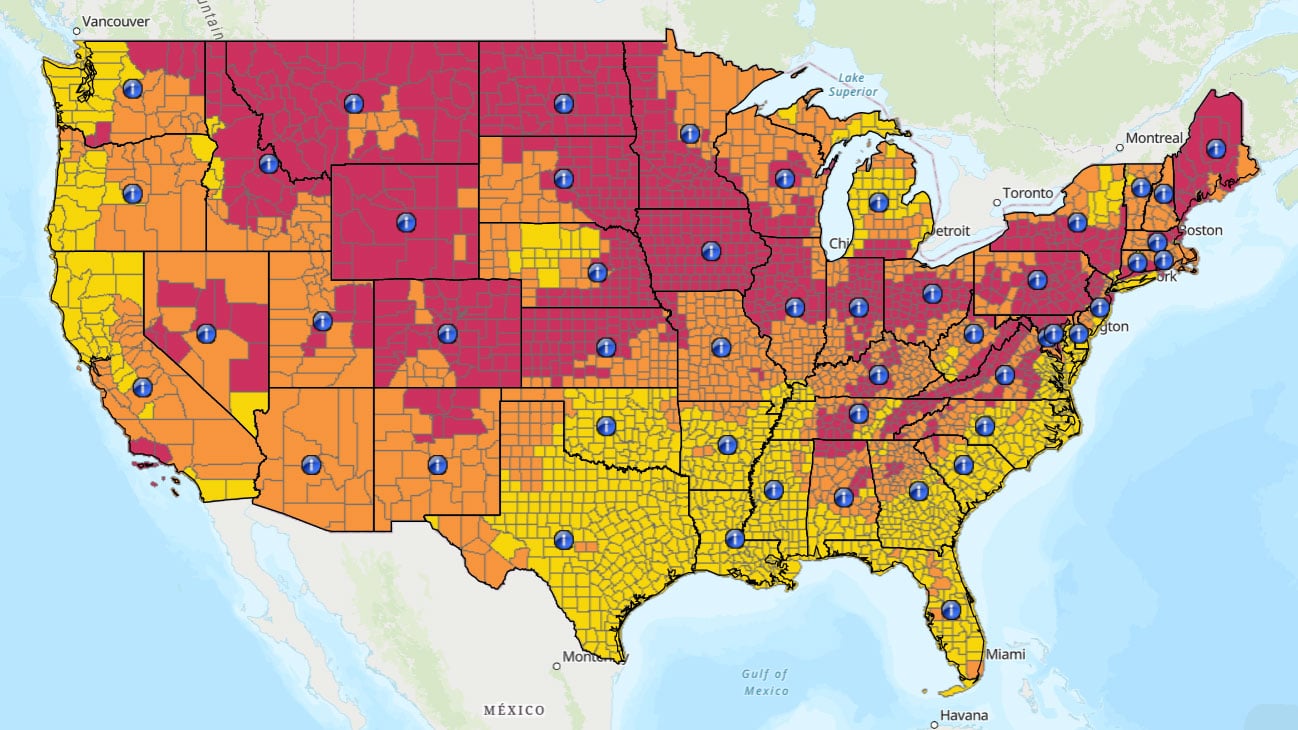
What is Radon?
Radon is a radioactive element that is part of the radioactive decay chain of naturally occurring uranium in soil. It cannot be seen and does not have an odor or taste. Radon exposure presents possible health effects including potentially lung cancer.
USEPA Radon Action Level
The United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) action level for radon is 4.0 picocuries per liter of air (pCi/L). The risk of developing lung cancer at 4.0 pCi/L is estimated at about 7 lung cancer deaths per 1000 persons. That is why USEPA recommends reducing your radon level if the concentration is 4.0 pCi/L or more.
Radon has been recognized by USEPA as a potential risk to occupants of buildings, most significantly residences. For areas occupied for residential use where levels of radon are measured at 4.0 pico-curies per liter or higher, USEPA indicates that mitigation measures should be implemented to reduce radon levels in indoor air.
Lender Requirements for Residential Radon Mitigation
The drive to reduce radon levels in homes is generally regulated at the State level or by lenders providing financing for the purchase of land and buildings. Lenders such as Housing and Urban Development (HUD) require certified measurement personnel regardless of state requirements. Due to the potential liability and health effects of radon on indoor air, this is a trend that will continue and increase across the lender base. Lenders such as Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac leave the decisions to test for radon up to the environmental professional.
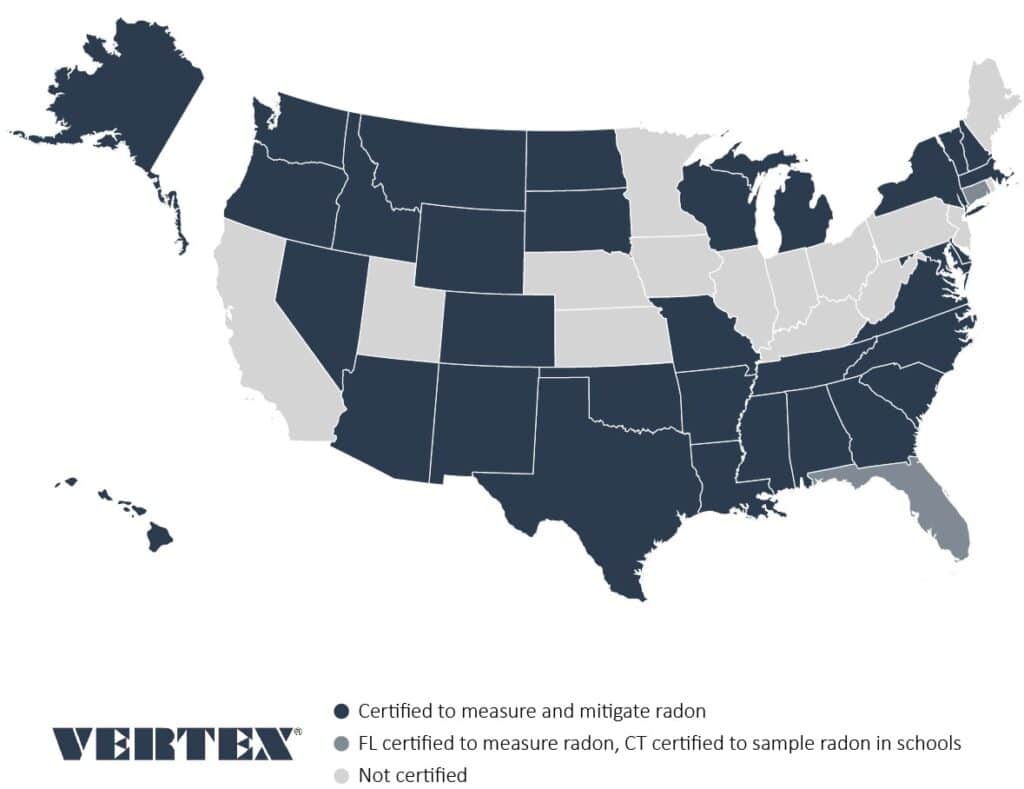
State Radon Regulations and Requirements
States may have their own regulations or have incorporated radon reduction requirements into their building code. The USEPA and the majority of states with regulations reference ANSI standards produced by the American Association of Radon Scientists and Technologists (AARST) standard. The AARST list of standards includes:
- Protocol for the Collection, Transfer and Measurement of Radon in Water
- Protocol for Conducting Measurements of Radon and Radon Decay Products in Homes
- Soil Gas Mitigation Standards for Existing Homes
- Protocol for Conducting Measurements of Radon and Radon Decay Products in Multifamily Buildings
- Radon Mitigation Standards for Multifamily Buildings
- Protocol for Conducting Measurements of Radon and Radon Decay Products In Schools and Large Buildings
- Radon Mitigation Standards for Schools and Large Buildings
- Rough-In of Radon Control Components in New Construction Of 1 & 2 Family Dwellings And Townhouses
- Reducing Radon in New Construction of One & Two Family Dwellings And Townhouses
- Soil Gas Control Systems in New Construction of Buildings
- Performance Specifications for Instrumentation Systems Designed to Measure Radon Gas in Air
- Radon Measurement Systems Quality Assurance
Radon Certification for Professionals
One commonality is the requirement and/or recommendation to hire certified personnel and companies who perform radon measurement, mitigation, or laboratory analyses. Certification is available for a variety of radon-related activities:
- Residential Radon Measurement – Certification for the testing of residential homes. Certification required completion of a 16-hour training program and passing a proficiency examination.
- Residential Radon Mitigation – Certification for the testing of residential homes. Certification required completion of a 16-hour training program and passing a proficiency examination.
- Multifamily Radon Measurement – Requires the residential certification, and an additional 8-hours of training.
- Multifamily Radon Mitigation – Requires the residential certification, and an additional 8-hours of training.
- Radon Resistant New Construction (RRNC) – Requires the residential certification and an additional 8-hours of training.
- Laboratory and continuous radon monitor usage – Laboratories and personnel who use field instruments to measure radon to evaluate potential exposure are required to complete additional training and submit certification of instrumentation and methods to AARST-NRPP at least annually.
The training programs also require that radon professionals obtain at least 24 credits of continuing education every 2 years and to submit certificates of completion of the continuing education along with the renewal application to AARST-NRPP.
States such as Florida require that persons providing technical support and advice related to radon (i.e., performing the work, interpreting the results, or providing consulting for work done by others) receive state-specific training and certification in addition to other such certifications identified earlier. Furthermore, radon professionals may also be required to maintain separate certifications (such as a general contractor’s license) to perform certain radon activities within a state.
Radon Sampling Requirements
A common question: What are the radon sampling requirements for my project?
The following highlights the requirements that apply to multi-family buildings, where VERTEX has extensive experience:
| PROPERTY TRANSACTION | NON-PROPERTY TRANSACTION |
| 100% First Floor Lowest space that now or in the future could be used as a residential space, including unfinished spaces. | 100% First Floor Lowest level currently used as a residential space. |
| 10% Upper floors | 10% Upper Floors |
| 100% Duplicates | 10% Duplicates |
| Duplicates are counted floor by floor, not in aggregate. Floors with 12 units would require 2 duplicates per floor. |
There are other quality control samples required most commonly blanks and spike samples that are also based upon the number of locations and/or detectors used at each site.
In states that do not have radon regulations the “requirement” to sample is most commonly driven by lenders or property owners as a risk management decision. In states like Massachusetts, property owners are required to provide a safe environment for their tenants the level of testing has varied depending on client risk tolerance. Lenders such as HUD have recently been requesting that at a minimum the non-property transaction protocol be followed. Other lenders seem to be leaning more towards the conservative side when it comes to radon testing.
Personnel certified to provide radon measurement services are required to note any deviations from the ANSI standards and the potential data gaps those may pose to a property owner. The information should be shared openly and clearly so that the property owner understands the risks and the limits of the requested sample data.
How Can VERTEX Help?
If you have questions about radon sampling or mitigation at any of your project sites please reach out to VERTEX and our certified radon experts will be happy to assist you in developing your radon measurement or mitigation strategies.
To learn more about our Environmental Consulting services or to speak with an Environmental Expert, call 888.298.5162 or submit an inquiry.
Author: JESSE FREEMAN PE, LSP