As weather patterns continue to change, it is becoming increasingly imperative to protect natural vegetation and the environment. One major contributor that causes many negative environmental impacts is erosion. Erosion is a geological process in which earthen materials (i.e., soil, rocks, sediments) are worn away and transported over time by natural forces such as water or wind; sometimes this is sped up by poor management or other human impacts on land. [1]
WHY ARE EROSION CONTROL MEASURES IMPORTANT IN CONSTRUCTION?
The potential for erosion is at its highest during construction due to the necessity for soils to be exposed during the construction process. If proper erosion control measures are not in place during construction there is potential for many negative impacts to the environment including polluted waterways, reduction in quantity and quality of topsoil necessary for agriculture, increased flooding potential, and more. In addition to reducing environmental impacts, proper erosion control measures are requirements to acquire local, state, and federal permits necessary for construction.
The following highlights a few commonly used erosion control measures.
TYPES OF EROSION CONTROL MEASURES
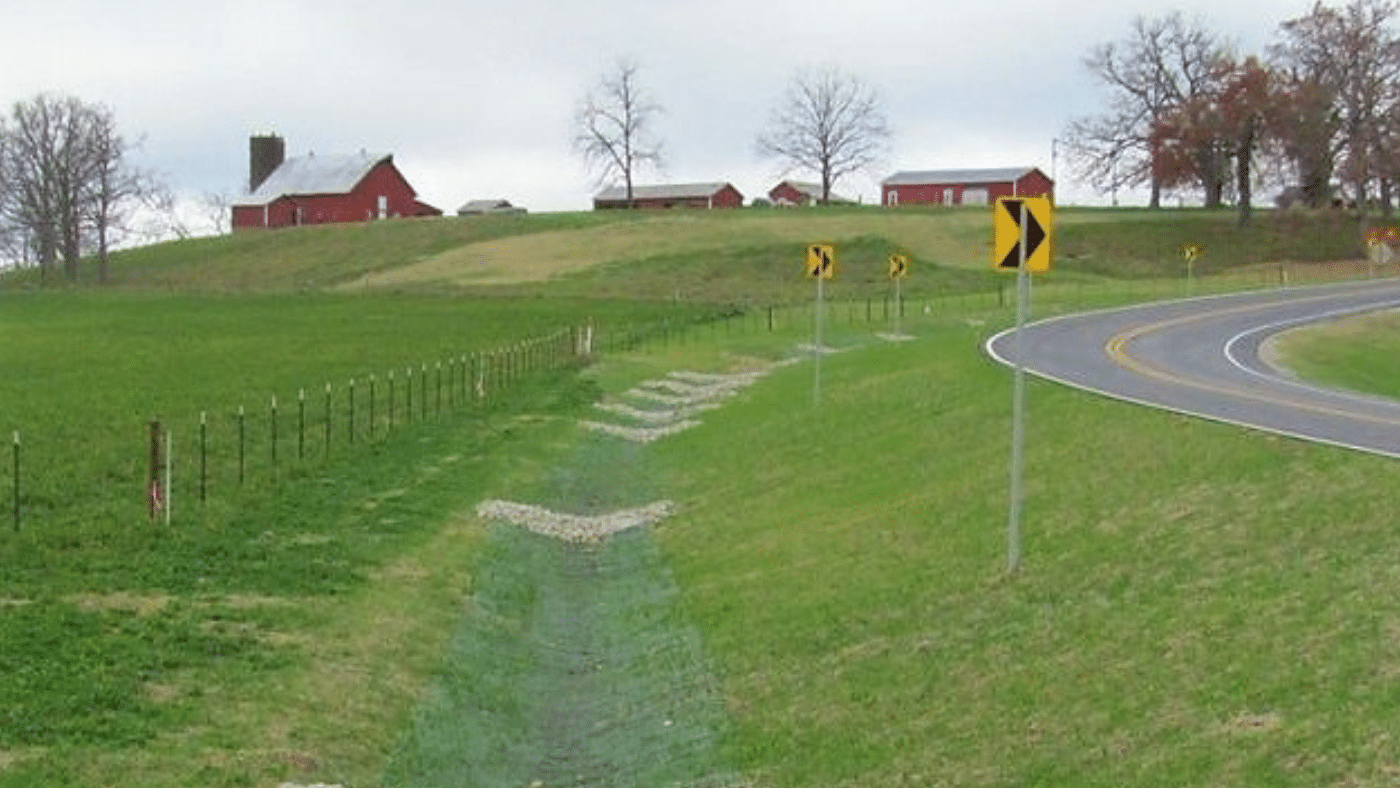
Sediment Basins and Rock Dams
A sediment basin refers to a pool formed in an excavated or natural depression with an earthen embankment where sediment can settle. Rock dams use rock and gravel as an embankment instead of compacted soil. [2]
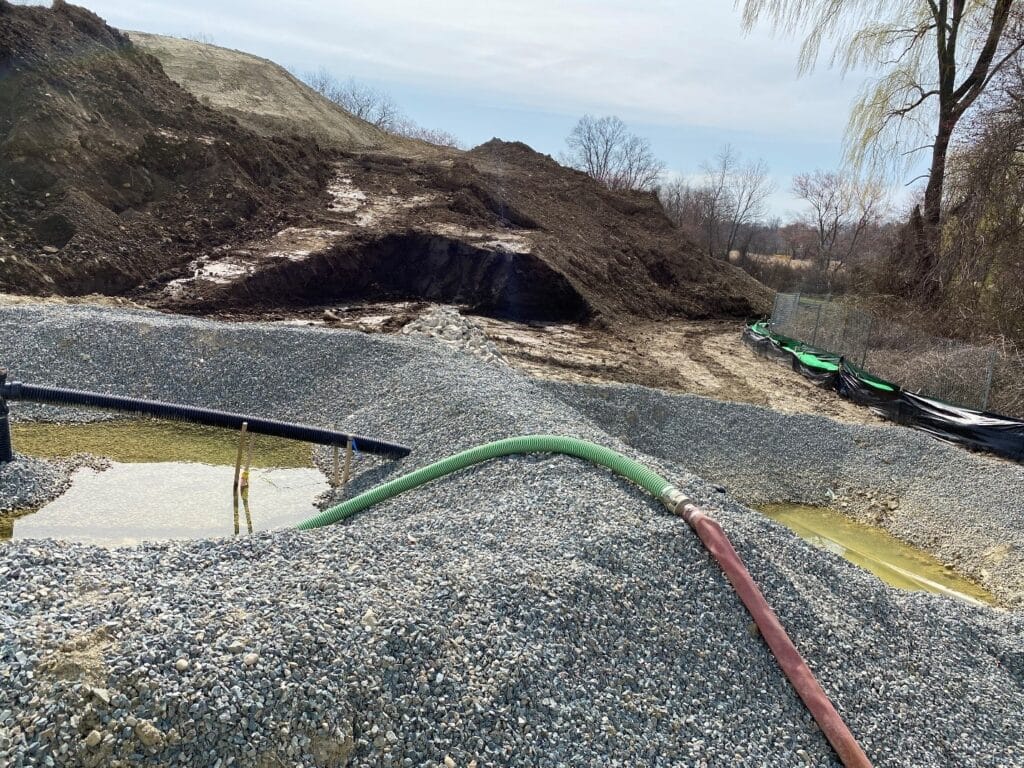

Figure 1: Rock Dam at William L. Foster Elementary School in Hingham, MA
Vegetated Filter Strip
Vegetated filter strips (also referred to as filter strips, grass buffer strips, and grass filters) are uniformly graded vegetated surfaces that receive runoff from adjacent impervious areas and slow runoff velocities, trap sediment, and promote infiltration. [3]
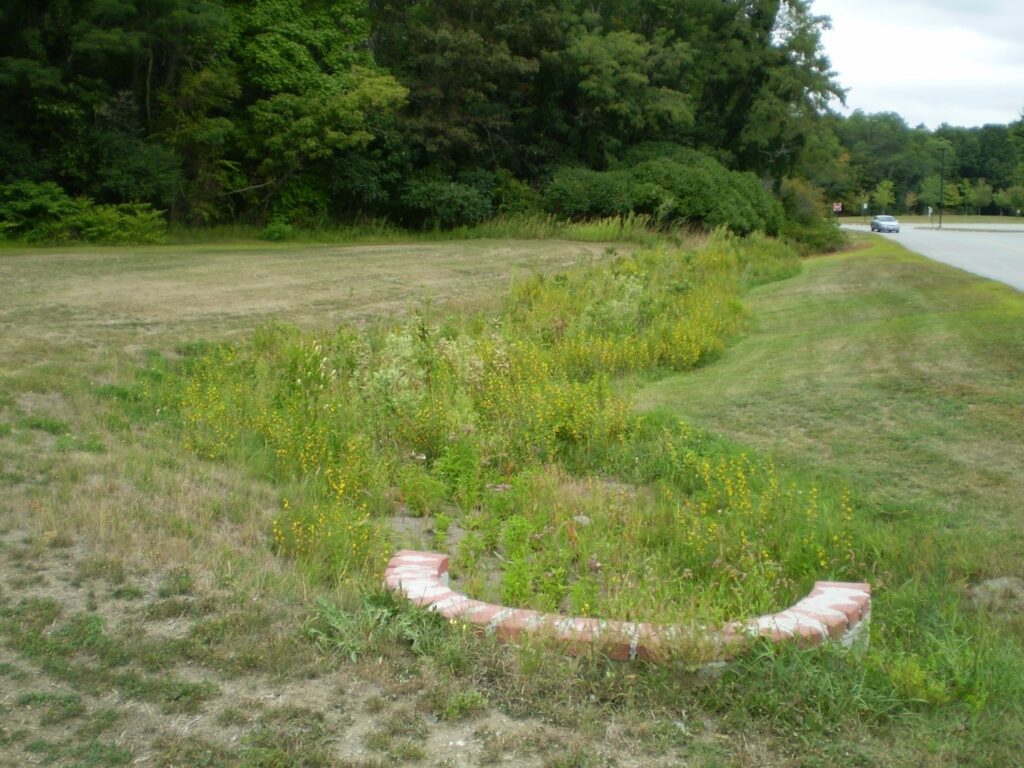

Figure 2: Example of a vegetated filter strip [3]
Silt Fence
A silt fence is a temporary sediment barrier made of porous fabric that is held up by wooden posts driven into the ground to retain soil on a construction site. [4]
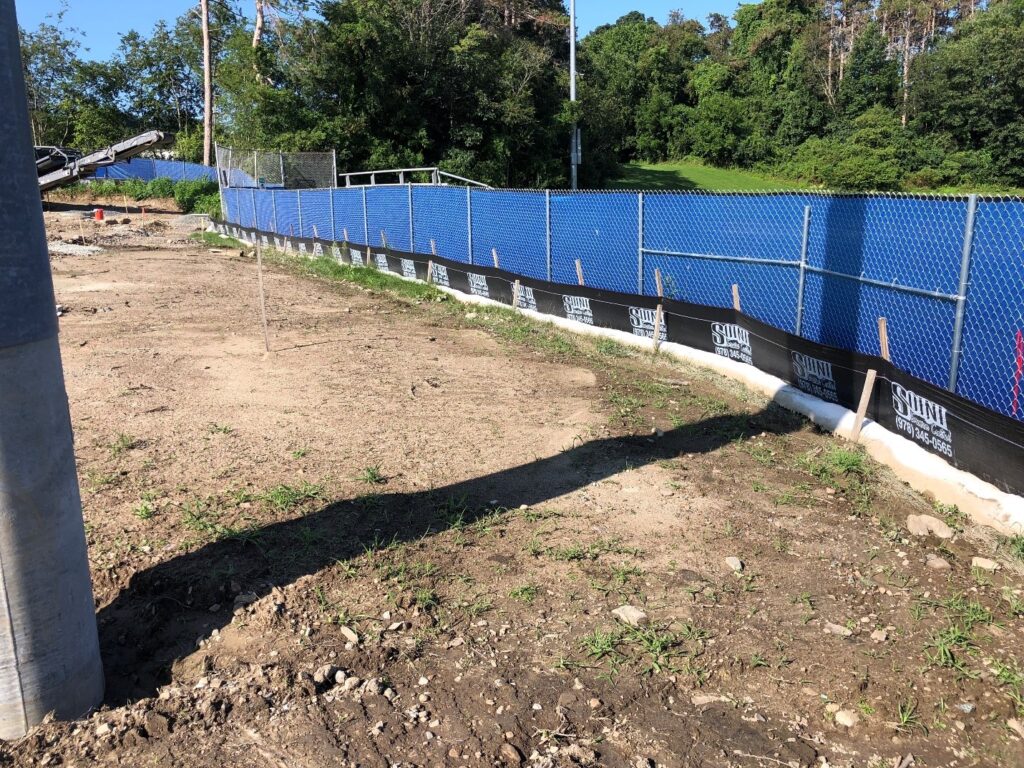

Figure 3: Silt fence and compost filter sock (see below) at Coakley Middle School in Norwood, MA
Compost Filter Socks
A compost filter sock is a mesh tube filled with compost material that is placed perpendicular to the direction of sheet flow to control erosion and retain sediment in disturbed areas. [5]
Check Dams
Built from stone, sandbags, or logs, a check dam is a small dam constructed across a drainage ditch, swale or channel to reduce flow velocity and allow retention of sediments. [6]
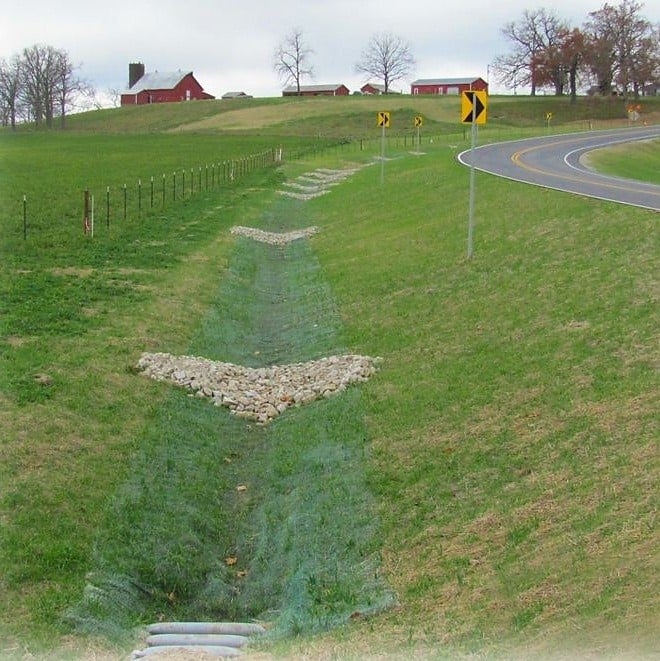

Figure 4: Example of stone check dams [6]
Inlet Protection
Inlet protection is a sediment filter or an excavated impounding area around a storm drain, drop inlet, or curb inlet to prevent sediment from entering storm drainage systems. Types of inlet protection include: straw or hay bale barriers, excavated drop inlet trap, gravel and wire mesh filter, block and gravel inlet protection, fabric drop inlet protection, and sod drop inlet protection. [7]
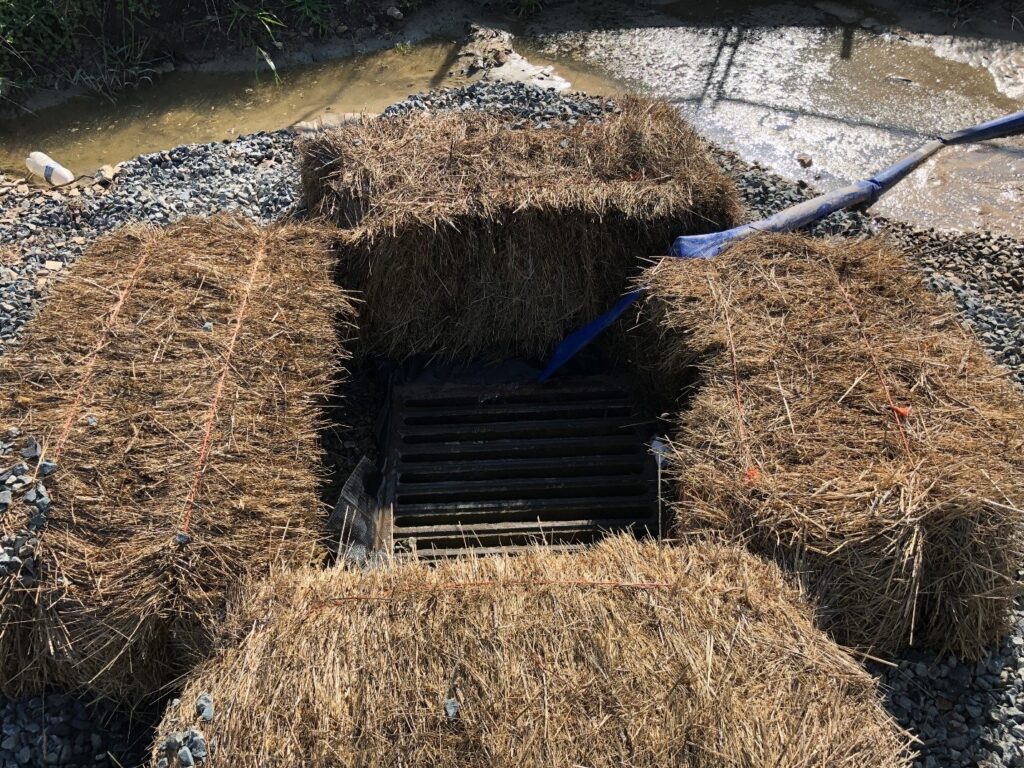

Figure 5: Hay Bale Barrier at Coakley Middle School in Norwood, MA
Stabilized Construction Entrance
A stabilized construction entrance refers to a temporary stone-stabilized pad located at points of vehicular ingress and egress on a construction site and provides a stable entrance/exit to keep mud and sediment off public roads. [7]
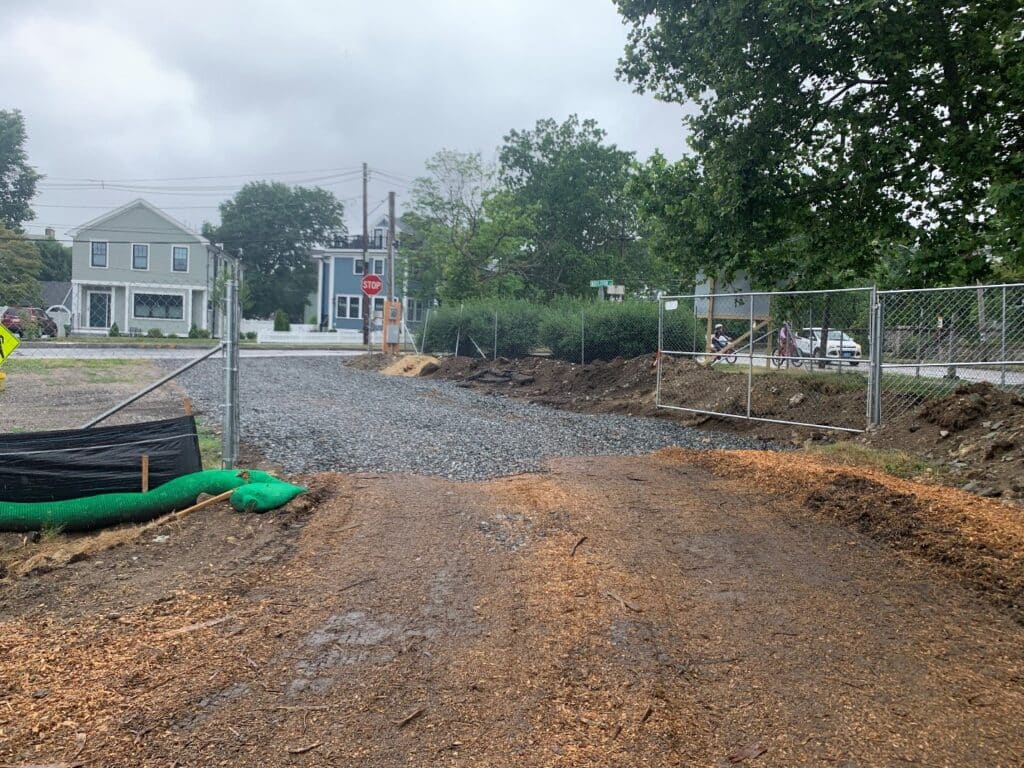

Figure 6: Stabilized Construction Entrance at Hosmer Elementary School in Watertown, MA
Outlet Protection and Stabilization
Outlet protection and stabilization refers to a structure designed to control erosion at the outlet of a channel or conduit by reducing the velocity of flow and dissipating the energy. [7]
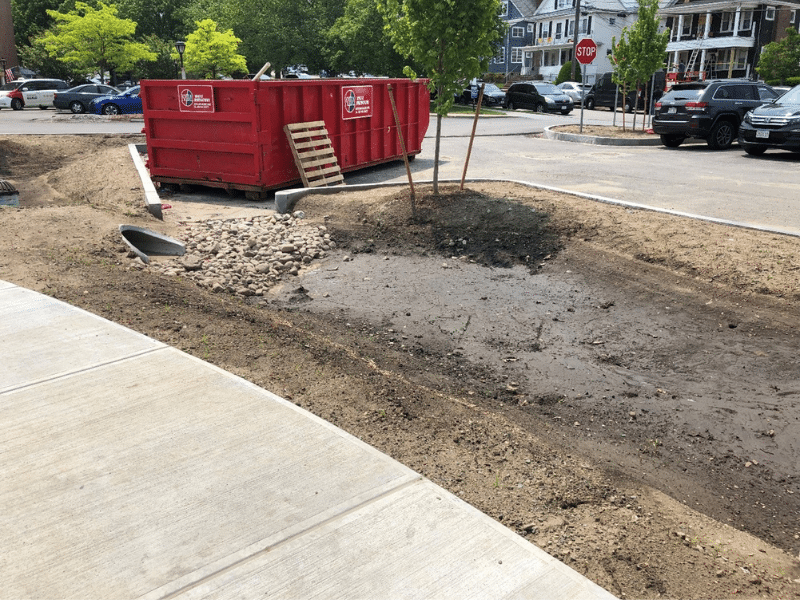
Figure 7: Outlet Protection and Stabilization at Hosmer Elementary School in Watertown, MA
Temporary or Permanent Seeding
Establishing vegetative cover on disturbed areas provides stabilization to the soil by holding soil particles in place. [7]
Level Spreader
A level spreader refers to an excavated depression constructed at zero percent grade across a slope to change concentrated flow into sheet flow discharged at non-erosive velocities. [7]
Preserving Natural Vegetation
Erosion can be minimized by limiting the amount of soil exposed and preserving the natural vegetation as much as possible.
WHY VERTEX?
Choosing an experienced engineer to design the proper erosion and sedimentation control measures for a given project is essential.
VERTEX has civil engineers across the country who are experienced in achieving local, state, and federal regulation requirements for erosion and sedimentation control. VERTEX’s team has successfully implemented designs for a multitude of commercial, industrial, and institutional developments.
To learn more about VERTEX’s Civil Engineering Services, or to speak with an Engineering Expert, call 888.298.5162 or submit an inquiry.
Resources:
[1] https://www.nrdc.org/stories/soil-erosion-101
[2] https://www.epa.gov/system/files/documents/2021-11/bmp-sediment-basins-and-rock-dams.pdf
[3] https://megamanual.geosyntec.com/npsmanual/vegetatedfilterstrips.aspx
[4] https://www.epa.gov/system/files/documents/2021-11/bmp-silt-fences.pdf
[5] https://www.epa.gov/system/files/documents/2021-11/bmp-compost-filter-socks.pdf
[6] https://megamanual.geosyntec.com/npsmanual/checkdams.aspx








